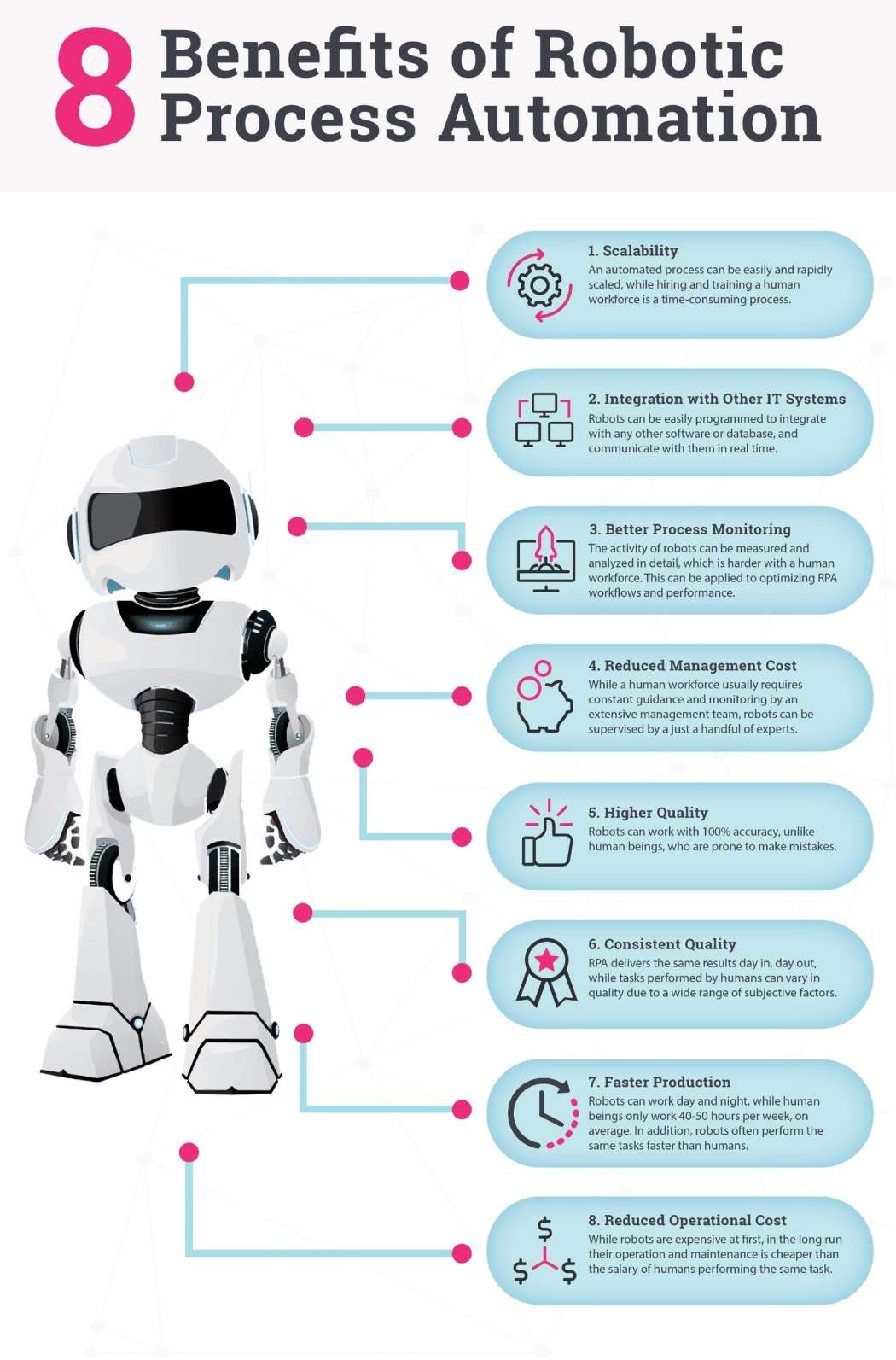
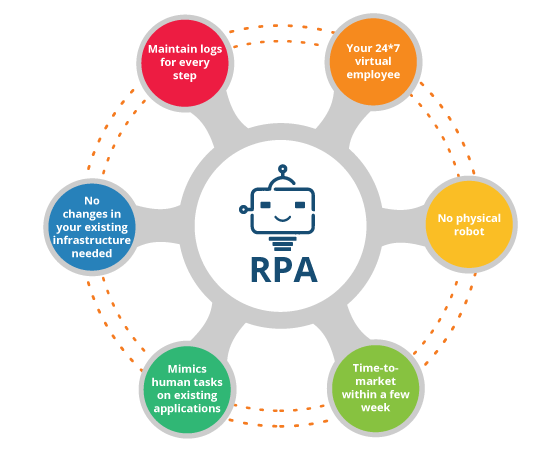
WHY Companies are excited about RPA solutions?
RPA Types
Programming options
RPA bots need to be programmed and there are a few ways to program bots which involve trade-offs between complexity of bots and programming time
Cognitive capabilities
Programmed bots need to have cognitive capabilities to determine their actions based on inputs they gather from other systems. RPA tools provide a range of cognitive capabilities
Usage
Bots serve specific functions. Though most RPA tools can be used to build bots that serve all these functions, some tools are more optimized for attended or unattended automation. While unattended automation is batch-like background processes, in attended automation users, for example customer service reps, invoke bots like invoking macros.
In our bank we have people doing work like robots. Tomorrow we will have robots behaving like people. It doesn’t matter if we as a bank will participate in these changes or not, it is going to happen.
John Cryan, CEO of Deutsche Bank